Immersive virtual reality is a concept that aims to influence users’ perception of reality within digital or computer-generated environments.
Various tools and techniques are employed to develop virtual experiences that provide users with a sense of presence and the illusion of realism in VR.
However, like other terms associated with the metaverse, the definition and interpretation of immersive virtual reality lacks a precise consensus.
While there are several reasons for this ambiguity, the primary factor remains the development of virtual environments using multiple components and enabling technologies.
This often results in diverse experiences, influencing users’ subjective perception of immersion in VR.
Proponents of VR technology argue for further classification, dividing immersive virtual reality into semi-immersive VR and fully immersive VR, depending on the inclusiveness of sensory stimulation within 3D environments.
Sensory stimulation plays a crucial role in immersing users in virtual worlds.
However, achieving fully immersive virtual experiences necessitates the consideration of other forms of immersion.
This article delves deeply into immersive virtual reality technology, factors influencing users’ subjective perception of reality, and the future possibilities of fully immersive virtual reality.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
Quick Navigation
What is Immersive Virtual Reality, and How Does it Work?
In the context of virtual reality, immersion refers to the ability of virtual experiences to immerse users in a digital environment such that it is difficult to differentiate between physical and virtual realities.
Immersive VR aims to provide a degree of realism where users can interact with their surroundings and feel physically present within virtual environments.
We hypothesize that sensory-motoric immersion, cognitive immersion, emotional immersion, and the role of gravity for spatial orientation, motion, and balance will aid fully immersive virtual reality.
Several studies have focused on enhancing the quality of both VR hardware and software components, as high-quality components are crucial for achieving a high degree of realism in VR, which can potentially influence how users perceive reality.
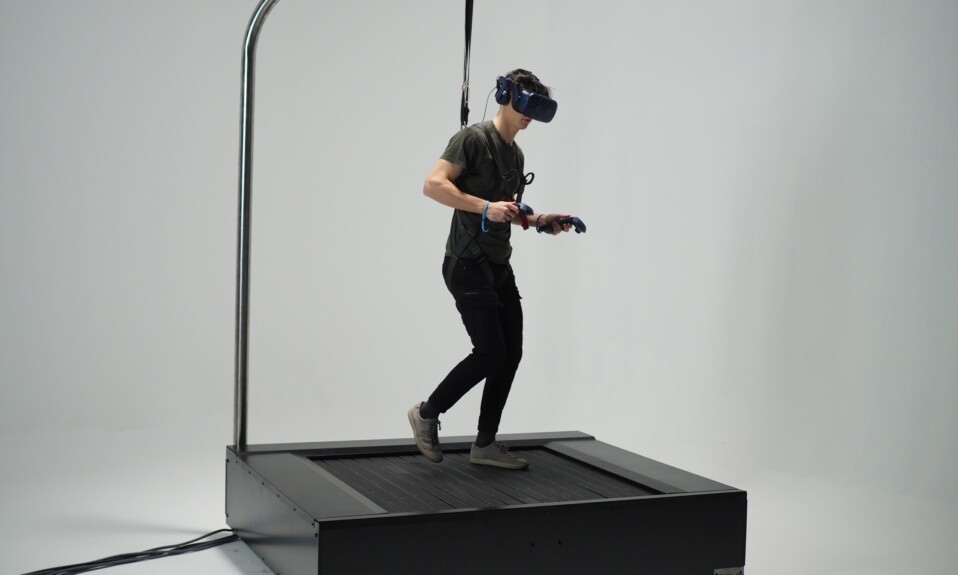
Devices such as omnidirectional treadmills, haptic suits, improved motion trackers, and hand controllers are incorporated with head-mounted displays to enhance user interactions in virtual reality.
Immersive VR attempts to replicate the human perception of physical reality in virtual worlds; therefore, it is imperative to understand the factors influencing the perception of the real world.
Understanding the Objective and Subjective Nature of Human Perception
Several forms of immersion collectively influence and actively shape how humans perceive the world and their surroundings.
The human perception of physical reality is an active process that combines multiple sensory inputs with complex brain processes, such as bottom-up and top-down processing.
Sensory inputs obtained from the five sense organs (eye for sight, ear for hearing, nose for smell, tongue for taste, and skin for tactile feedback) convert real-world information into electrical impulses sent to the brain through a process known as transduction.
The responses to stimuli from sensory organs form ‘Sensation,’ and their interpretations result in ‘Perception.’
When these electrical impulses reach the brain, they trigger various processes (the bottom-up and top-down processes).
Top-down processing utilizes existing mental models, prior knowledge, and past experiences to influence information processing.
Bottom-up processing takes sensory information from the present environment and builds it into perception.
Studies show that stimulation from one sense organ can significantly influence how information is perceived from the others, as sensory organs work together to build a unified perception of the world.
Though objective elements of reality exist, human perception is complex and subjective, making it difficult to accurately model and replicate detailed levels of immersion and such a degree of realism in virtual reality.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
What Are the Current Levels of Immersive Virtual Reality?
Despite current levels of technological advancement, no device delivers all the sensory stimulation needed for fully immersive virtual experiences.
Significant progress is ongoing in providing enhanced visual, auditory, and tactile feedback crucial for immersive virtual experiences.
There are models of virtual reality headsets consisting of arrays of sensors, lenses, eye trackers, and six degrees of freedom (6DoF) for improved head tracking and spatial audio technology.
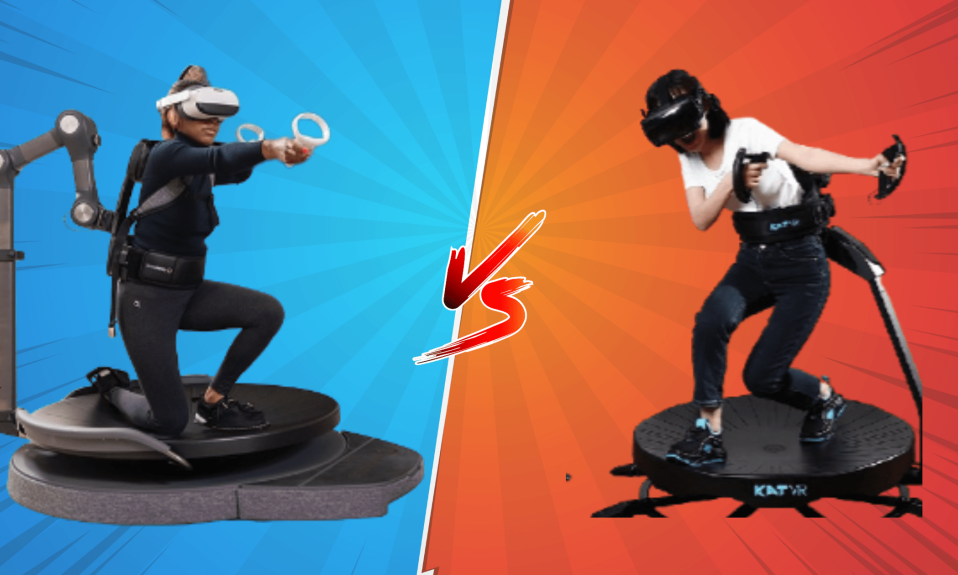
Omnidirectional treadmill simulators like the Omni One and the Kat Walk C2+ provide a low-friction locomotion interface for simulating physical motion such as walking, crouching, or running in virtual reality.
However, prolonged use of virtual reality often results in health complications such as migraines, dizziness, and nausea, attributed to cybersickness or motion sickness.
The absence of all basic human senses in VR causes conflicting signals and information mismatches in the brain.
Potential drawbacks also include stress from physical exertion, lack of quality content consideration for users, the bulky nature of VR hardware, and the amount of friction that occurs when setting up virtual experiences.
What Are the Future Possibilities of Immersive Virtual Reality?
VR enthusiast Prashant Kumar suggests that fully immersive virtual reality would comprise five essential pillars. They include a neural link, touch, smell, taste, and artificial intelligence.
In his 2019 TEDx Talk, he discussed various research and technological advancements that bring the possibilities of fully immersive virtual reality closer to fruition.
He highlighted the progress made with human-computer interaction using neural links, tactile or haptic feedback using e-skins, aroma diffusers for smell, and silver electrodes to mimic taste.
Additionally, he proposed a sentient AI to handle complex and computational processes.
A 2021 opinion piece suggests a two-dimensional approach, combining the “sense of being there” and “perceived realism” to enhance both realism and feelings of (tele)presence in virtual reality.
The publication attributes the ‘sense of being there’ to blocking out external stimuli and exposing users to visual and auditory sensory inputs provided by head-mounted displays.
Perceived realism is a technique for influencing the degree of realism within virtual environments by enhancing the nature and characteristics of objects, scenes, and the plausibility of events in VR.
However, other researchers believe that the true purpose of virtual reality lies not in replicating the real world but in providing opportunities for users to explore beyond the boundaries and limitations of physical reality.
Final Thoughts on Immersive Virtual Reality
Immersive virtual reality aims to create virtual experiences with some degree of realism that enables users to feel a sense of physical presence in virtual environments.
While the human perception of reality is subjective, there exist objective elements that provide a silver lining for immersive VR experiences.
Sensory stimuli play a crucial role in immersion, and several devices currently provide visual, tactile, and auditory information with some degree of realism.
Despite the progress made, the path toward realizing fully immersive virtual reality experiences remains intricate and constantly unfolding.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!