Whenever an emerging technology goes mainstream, it instantly triggers a hype cycle, attracting brands and corporations of various sizes looking to capitalize on such trends.
Mark Zuckerberg’s conceptualization of the metaverse and the subsequent rebranding of Facebook’s parent company to Meta Platforms made this evident.
In subsequent years, attention to the metaverse slowly declines as mainstream media pivots to other innovations and emerging technological solutions.
As the metaverse hype cycle fades into oblivion, brands and corporations whose intentions involve actively building and contributing to the growth of the metaverse ecosystem remain.
Hardware and software infrastructures that support virtual reality, augmented reality, the blockchain, and other metaverse-related technologies are undergoing significant and continuous improvement.
This article focuses on the applications of the metaverse in real-world scenarios, highlighting its current use cases, and ends with a note on future possibilities and applications.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
Quick Navigation
Quick Recap on the Definition of the Metaverse
Several definitions of the metaverse exist across the internet and the virtual ecosystem. Hence, some proponents argue that it has become somewhat of a loosely defined term.
As the metaverse unfolds, it is challenging to have a precise definition as many technological solutions and innovations contribute to its growth and advancement.
In our comprehensive guide on navigating the metaverse and virtual reality, we defined the metaverse as an immersive, shared, and persistent virtual experience created by the convergence of virtual reality, augmented reality, and the internet.
The metaverse is a realization of an idea, a unique point in time where the technologies that support interactive digital experiences merge into a shared, immersive, and persistent ecosystem.
The technological solutions embodying the true essence of the metaverse include extended reality technologies like virtual and augmented realities, decentralization as a function of the blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the internet.
Now that we have a definition of the metaverse, we explore its current applications and use cases to see what the future holds.
Applications and Use Cases of the Metaverse
The applications of the metaverse span various industries: the educational sector, retail and commerce, medicine and healthcare, gaming, real estate, and so on.
This section discusses the application of the metaverse in three prominent industries: education, healthcare, retail, and commerce.
Applications of the Metaverse in Education
Within the context of the metaverse, education is a broad categorization that comprises all learning activities, training exercises, and experiences that utilize the core technologies that embody the metaverse.
Early applications of virtual and augmented reality technologies date back to the 1900s as components of military training and flight simulations.
Today, metaverse technologies exist to enhance the quality of both formal and informal education across a myriad of industries.
These industries include healthcare, information and communication technology, business and social communication, industrial training processes, etc.
In a 2021 study on the educational applications of the metaverse, researchers identified four use cases that suggest its potential as a tool for social communication, a higher degree of freedom to create and share, provision of new experiences, and enhanced immersion via virtualization.
With formal education, the metaverse can influence students’ performance by bolstering creativity and enhancing their thinking capabilities using social and personalized interactive learning experiences.
Complex theories, structures, and illustrations challenging to conceptualize using traditional training materials like physical books and 2D illustrations can be accurately reproduced by leveraging virtual and augmented reality technologies.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
A 2019 study explored the applications of the metaverse in an educational setting to improve university students’ presentation and public speaking skills.
Using virtual reality gadgets and specialized software, the participants enhanced their presentation skills by minimizing filler words during speech and improving hand gestures.
Other metaverse platforms enable users to engage in interactive experiences through educational role-play by simulating virtual learning environments such as virtual classrooms and laboratories.
Zepeto and Foldit are examples of such platforms, utilizing virtual reality, augmented reality, 3D, and facial recognition technology to enhance learning experiences in the metaverse.
Applications of the Metaverse in Healthcare
Metaverse technologies have long been utilized in the healthcare industry to supplement medical training, aid surgical procedures, improve psychotherapy, and enhance patient-clinician relationships.
Most recently, the Apple Vision Pro, a mixed-reality headset used during two successful micro-surgical spine procedures in the U.K., raised awareness for metaverse technologies in the medical field.
A 2022 survey on the applications of the metaverse in healthcare highlighted seven major domains representing its uses in telemedicine, clinical care, education, mental health, physical fitness, veterinary, and pharmaceuticals.
Data from the survey suggests that metaverse technologies for medical training and learning may constitute a significant portion of its applications in healthcare.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies create realistic 3D representations of complex organs, systems, and processes within the human body.
It enables students to understand the intricacies and navigate the human body through effective visualization and real-time interactions.
Students and physicians can practice surgical procedures and emergency response training like cardiopulmonary resuscitation in simulated digital environments.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
By utilizing such training environments, medical personnel can improve their precision and accuracy, enhancing their preparedness to tackle real-world problems.
Midwifery students at the University of Newcastle, Australia, utilize virtual reality technology to visualize the intricacies of pregnancy while navigating common issues such as breach positioning and placenta placement.
In telemedicine, the metaverse supports remote sessions and consultations between patients and physicians through interactive virtual or augmented reality experiences.
OptiVu is a mixed reality software developed by Zimmer Biomet (a medical device company) utilizing virtual and augmented reality technologies to provide holographic projections of 3D graphics and illustrations to the real world.
Physicians and patients can visualize affected body parts in real time, making it easier for patients to understand the scope and full extent of recommended surgical procedures.
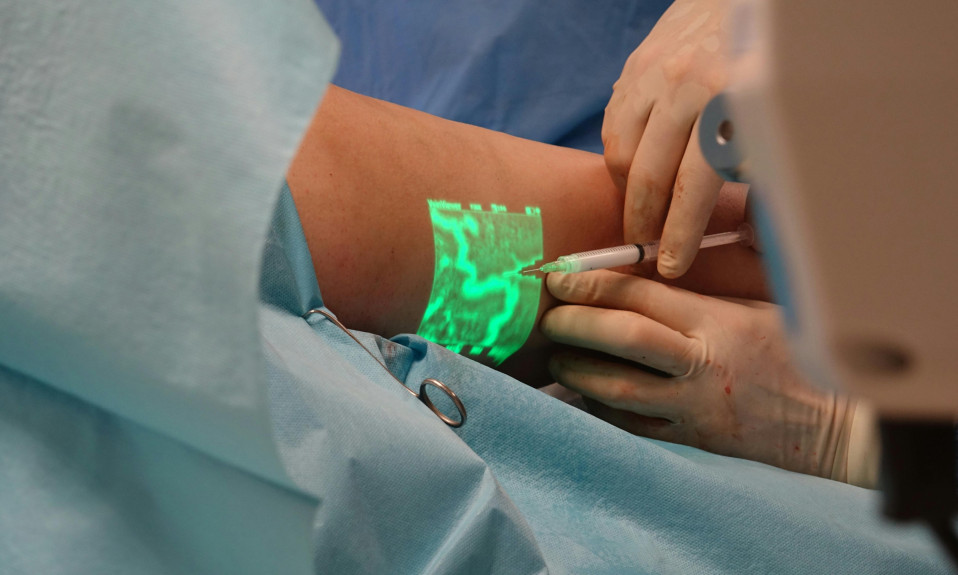
During clinical care, caregivers and physicians utilize devices that employ metaverse technologies such as the “Augmented Reality Vein Finder.”
Augmented reality vein finders employ projection-based AR and vein visualization technology to assist practitioners in finding, visualizing, and superimposing a map of a patient’s vein onto their skin.
Other applications in medicine and healthcare include its use for physical fitness, distraction therapy, concussion discovery, aid during surgical procedures, and so on.
Applications of the Metaverse in Retail and Commerce
The transition from physical to online shopping (e-commerce) over the past few years shows the potential of the metaverse in influencing how consumers shop.
“Consumers are increasingly seeking more immersive experiences and demanding the ability to interact with products and brands before making a purchase.”
-McKinsey
During the metaverse hype cycle, shopping in the metaverse was widely believed to revolve around virtual goods only accessible using metaverse technologies.
The story is quite different today, as data reveals that consumers are majorly interested in metaverse shopping experiences that are augmented and tied in with physical products in the real world.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies bridge the gap between physical (in-store) and online shopping by providing immersive and interactive shopping experiences.
Shopping experiences within the metaverse include four major categories: virtual try-ons, real-world overlay, virtual showrooms, and augmented reality mirrors.
Through these categories, consumers can engage in pre-buying behavior and processes thought to be only possible in physical shops.
Virtual try-on is applicable in the fashion and beauty industries, enabling consumers to try out different outfits, shades of makeup, and hairstyles using augmented reality experiences to make informed purchase decisions.
With a real-world overlay, interactive 3D versions of physical products are superimposed or projected onto the real world, enabling consumers to visualize the products in real time.
Brands can showcase their products in virtual showrooms using 3D objects, images, videos, or illustrations within digital platforms and virtual environments.
These experiences can be accessed using mobile devices and head-mounted displays (HMDs) such as VR or MR headsets.
Sephora, IKEA, and Mac Cosmetics are popular brands that utilize metaverse technologies to reduce friction and enhance consumers’ purchase journeys.
Final Thoughts on Applications of the Metaverse
The metaverse promises to be a game changer and the next version of the internet that will provide interactive and immersive digital experiences.
Consumer brands, universities, and healthcare institutions utilize metaverse technologies to enhance healthcare services and learning experiences and streamline consumers’ purchase process.
Unsurprisingly, learning and education constitute a significant part of metaverse applications across several industries.
It correlates with a study by Sortlist that reveals the second largest investment in the metaverse among participating brands was in the educational sector.
While it is evident that there are many use cases for metaverse technologies, it is necessary to explore user preferences and the efficiency of these applications.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!