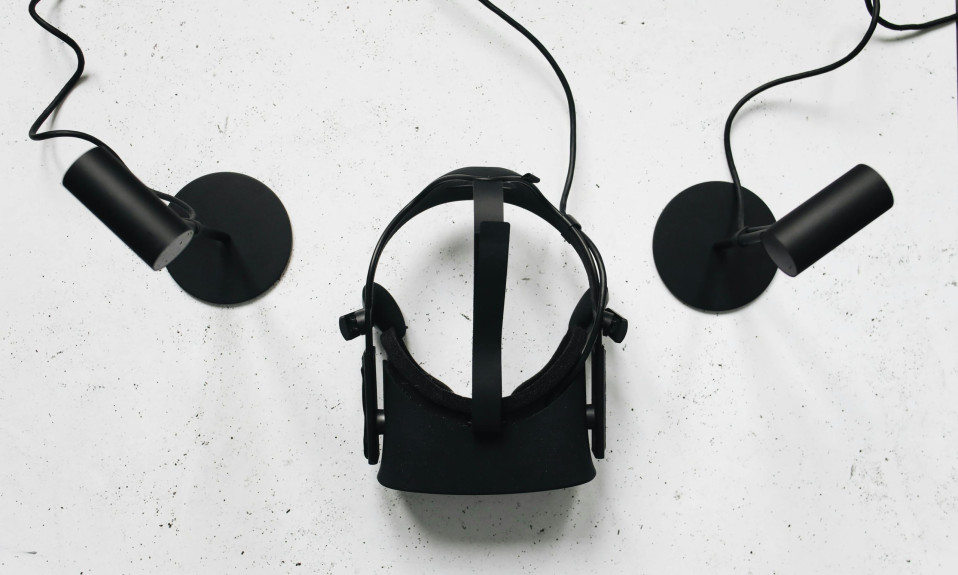
Virtual reality and the metaverse are terms often used interchangeably to describe computer-generated or simulated digital environments.
While both terms are closely related, virtual reality constitutes the core technologies or building blocks that embody the metaverse.
This fueled several debates over the existence of the metaverse, considering the vast number of virtual reality experiences that exist today.
A 2022 trend report shows well over 500 brands actively building various facets of virtual reality within the metaverse ecosystem.
The concept of virtual reality began in the late 1900s, but the term was coined in 1987 by Jaron Lanier, who made several notable contributions to the evolving VR industry.
In our beginner’s guide to the metaverse, we defined the metaverse as an immersive and persistent shared virtual experience created through the convergence of virtual reality, augmented reality, the blockchain, and other core technologies.
Without a doubt, virtual reality is crucial. It remains the foundation and underlying framework for building fully immersive metaverse experiences.
In this article, we delve into the nitty-gritty of virtual reality and its role in shaping the metaverse ecosystem.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
Quick Navigation
What is Virtual Reality?
Several definitions of virtual reality exist, all shaped by different perspectives on what constitutes the essence of VR and its enabling technologies.
The growing body of research suggests two primary schools of thought for defining virtual reality.
The first school defines virtual reality based on three core properties: telepresence, interactivity, and immersion.
While the second categorizes virtual reality into two broader categories: immersive virtual reality and non-immersive virtual reality.
However, the perception of physical presence and the interaction with digital elements within simulated environments, contribute to an enhanced feeling of immersion in virtual reality.
So, how do we define virtual reality?
Virtual reality is an immersive experience where users operate in a computer-simulated digital environment using virtual reality gadgets, personal computers, mobile phones, and other related tools.
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
Virtual reality utilizes various technologies, software programs, and hardware devices to create and simulate computer-generated environments for different purposes with varying degrees of immersion.
In the early stages of virtual reality development, military training, flight, and automobile simulations were some of its uses alongside other applications within the medical industry.
To better understand how virtual reality works, we consider the second school of thought, categorizing virtual reality into immersive and non-immersive VR.
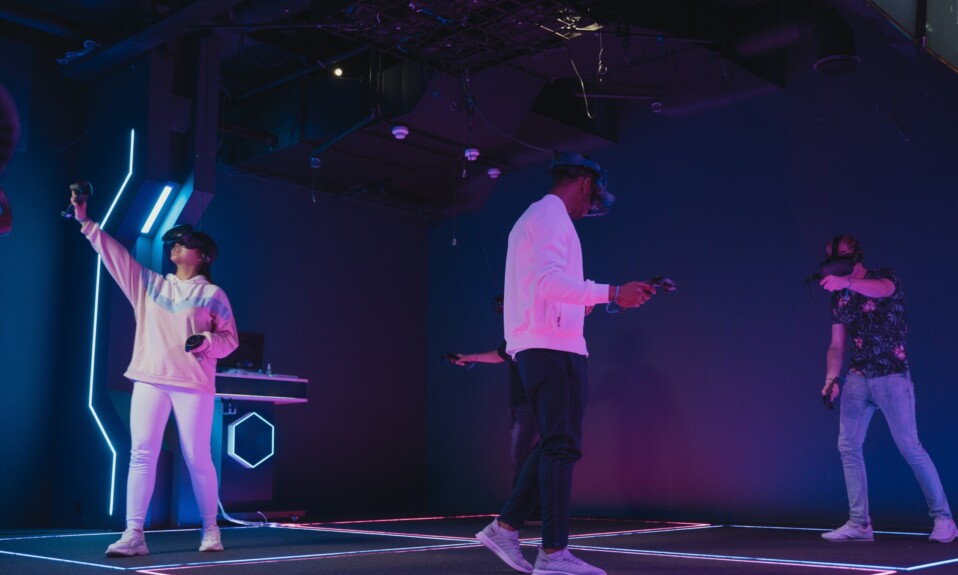
Immersive virtual reality experiences involve head-mounted displays with binaural or spatial audio to simulate three-dimensional (3D) virtual worlds or environments.
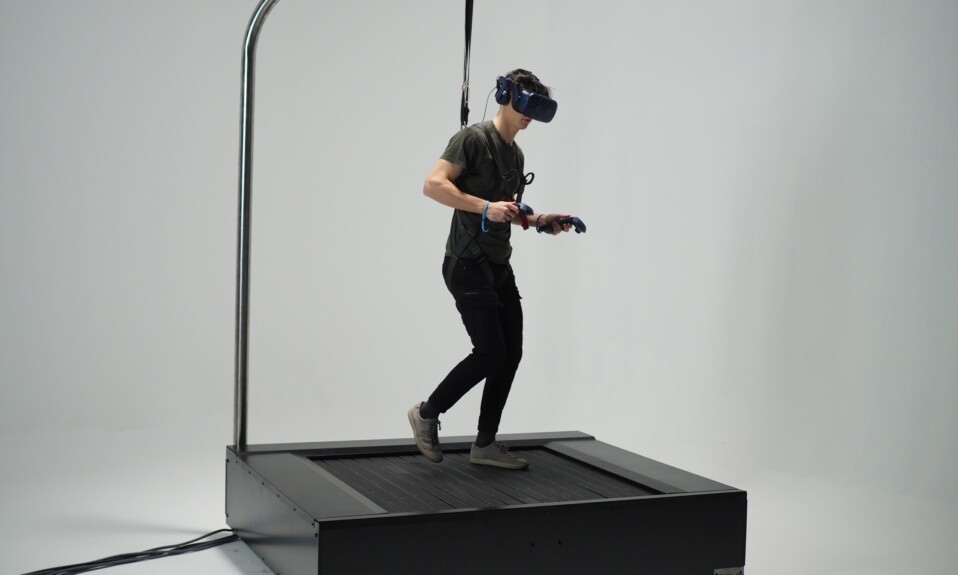
These experiences may also employ relevant virtual reality gadgets such as VR hand controllers, haptic suits, VR omnidirectional treadmills, and so on for improved immersion.
With non-immersive virtual reality experiences, virtual environments get rendered on 2D screens for mobile and desktop devices.
As a result, the perception of presence and immersion are significantly reduced.
Nevertheless, non-immersive virtual reality experiences offer vast user experiences ranging from 2D Scenes to fully rendered 3D worlds.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
What are Head-mounted Displays (HMDs)?
Head-mounted displays (HMDs) are devices worn on the head or mounted on helmets, rendering virtual environments and simulations on special screens or projecting digital elements onto the real world.
The most recognized head-mounted display (HMD) device that laid the groundwork for virtual reality gadgets and devices is the Sword of Damocles, developed by Ivan Sutherland in 1968.
Three popular consumer-grade head-mounted displays include the Meta Quest (Oculus) VR headsets, the HTC Vive virtual reality headset, and the Apple Vision Pro headset, blending VR and AR into a mixed-reality experience.
Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets:
Virtual reality headsets are head-mounted displays that utilize sensors, screens, lenses, spatial or binaural audio, and controllers to simulate immersive experiences of varying degrees in virtual reality.
The launch of the Oculus Rift in 2016, alongside consumer-grade virtual reality headsets like the HTC Vive, brought widespread interest to explore and build out virtual reality experiences.
Statistics from a 2022 survey of over 4,000 U.S. adults show that lower-priced virtual reality headsets are the primary factor influencing the use of the metaverse.
However, concerns exist about the health effects of prolonged VR use, which can cause discomfort like eye fatigue, motion sickness, headaches, and severe cases of seizures.
The Role and Applications of Virtual Reality in the Metaverse
Gamers and tech enthusiasts are widely considered the early adopters of virtual and augmented reality experiences within the metaverse ecosystem.
However, history tells a different story, as there has been a lot of involvement and utilization of these technologies by government organizations such as the military and space exploration agencies.
During World War II and the 1900s, interactive 3D environments, cameras, projectors, and flight simulators were part of military training.
Today, virtual reality applications are in education, business, entertainment, gaming, tourism, real estate, behavioral sciences, and the medical industry.
To paint a clearer picture of the role and involvement of virtual reality technologies in shaping the metaverse ecosystem, we highlight its use and application in two prominent industries: Education and The Field of Medicine.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
Applications of Virtual Reality in the Educational Sector
Virtual reality is increasingly utilized in colleges and universities as a content delivery platform to improve creativity and promote heightened thinking capabilities among students.
A study was conducted in 2019 among seventy-one (71) university students (39 males and 32 females) to uncover the potential of virtual reality in helping students improve their presentation and public speaking skills.
Participants had no prior experience with the dedicated VR software program, nor had they ever used any virtual reality application in an educational setting.
The VR application utilized during the study was Ovation VR, which enabled the participants to practice their communication and presentation skills in an interactive and immersive virtual environment.
After establishing a baseline of the students’ performance (words per minute, hand gestures, and use of filler words) during a trial presentation, the students had to deliver the presentation a second time.
Overall, the study results showed significant improvement in the participants’ presentation skills, particularly in using fewer filler words and improved hand gestures to display confidence and control.
Another study conducted by Sortlist among 200 brands invested in the metaverse reveals that brands in the educational sector contribute the second-largest percentage (12%) of investment in the metaverse.
It shows lots of potential and growing interest from brands in building virtual and augmented reality experiences for education and enhancing learning opportunities in the metaverse.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Medicine and Healthcare
Over the years, virtual reality and its related technologies have proven to be a valuable resource in the medical field, psychology, and behavioral sciences.
There are virtual reality experiences and applications developed to help patients with mental health concerns like psychotic disorders and anxiety disorders like phobias and PTSD.
A 2019 review of existing literature on virtual reality in the medical context identified fourteen (14) major application areas of virtual reality in the medical field.
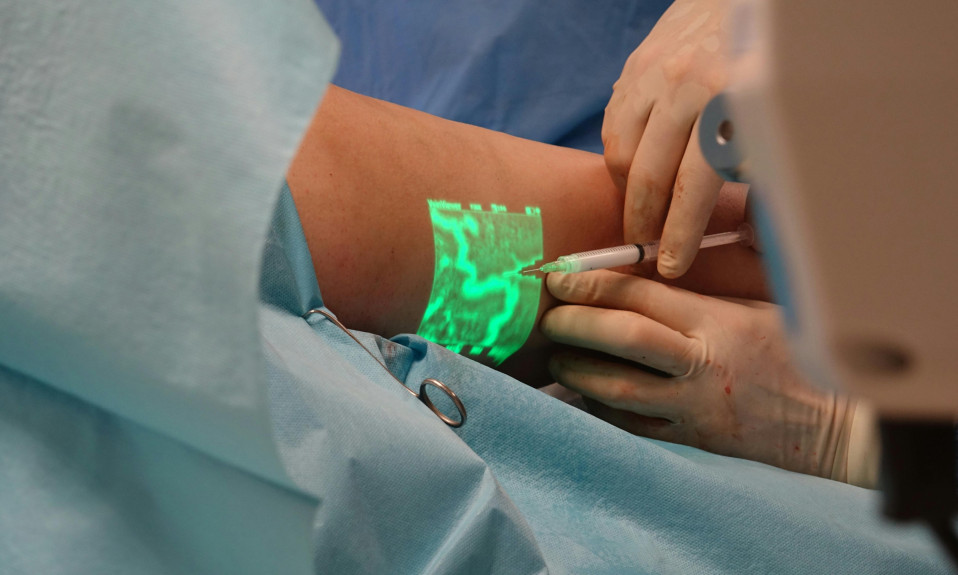
Medical practitioners and students can perform risk-free medical procedures and surgeries in virtual reality to improve their accuracy and gain certain levels of experience.
Training programs can simulate emergencies and critical health conditions in virtual environments to test the abilities and skills of trainees.
Virtual reality experiences and applications enable medical students to visualize and interact with three-dimensional (3D) simulations of the human body and complex structures.
The future applications of virtual reality in the medical field are promising, as existing studies show the potential for enhancing knowledge and improving skill sets among practitioners.
I do not want a discount, said no one ever! Upgrade your VR setup today with top-tier accessories—use code META20 for 20% off + free shipping on orders over $15. Level up your VR experience now ➡️ Shop & Save!
Conclusion
Virtual reality and its related technologies have made invaluable contributions to humanity and the metaverse ecosystem.
What started as a tool for the military, automobile, aeronautics, and space exploration agencies during its infancy has rapidly grown into the gaming industry, medicine, education, tourism, and so on.
Compared to the 1900s, virtual reality experiences and applications today provide a greater sense of presence and immersion with new technologies and VR gadgets like haptic suits and omnidirectional treadmills like the Kat Walk C2+ and Virtuix Omni One.
Further insights from a survey of 1050 participants suggest that people are more willing to join the metaverse because of job opportunities, art and live entertainment, and monetary investments.
With brands actively invested in building the metaverse and incorporating elements of virtual and augmented realities into their culture, exciting possibilities lie ahead.